Web API security:
strategies and critical points
by Enrico Zimuel
Principal Software Engineer @ Elastic
FullStackConf 2019, Oct 10, Turin (Italy)
Anand Prakash

Facebook hack
- In 2016, Anand discovered a vulnerability in Facebook
- In Facebook you can reset your password using email or mobile phone
- A random code of 6 digits is sent to the email/phone
- You can try 10-12 time to insert this secret code
- After these attemps, Facebook blocks you
Facebook hack (2)
- Anand found that beta.facebook.com and mbasic.beta.facebook.com were missing the rate limit protection
- He was able to brute force the 6 digits code
- Anand received $15,000 from Facebook Bug Bounty program
Web API
From web application
To web API

Security implications
- A web API introduces more:
- Endpoints: more URLs to call
- Traffic: machine to machine
- Technologies: RPC, REST, SOAP, etc
- Formats: JSON, XML, etc
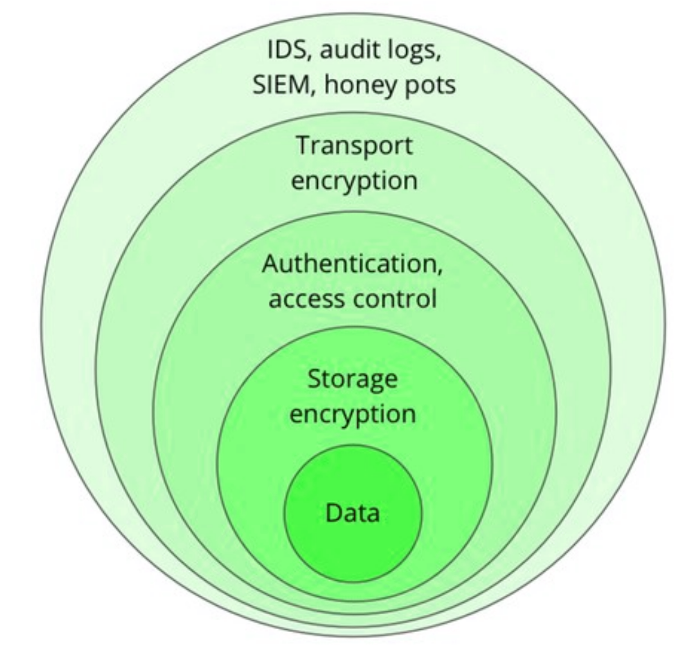
Defense layers
Logging & Monitoring
Logging & Monitoring
GDPR
- Detecting data leakage and alert users and controllers
- Art. 33, Notification of a personal data breach to the supervisory authority
- Art. 34, Communication of a personal data breach to the data subject
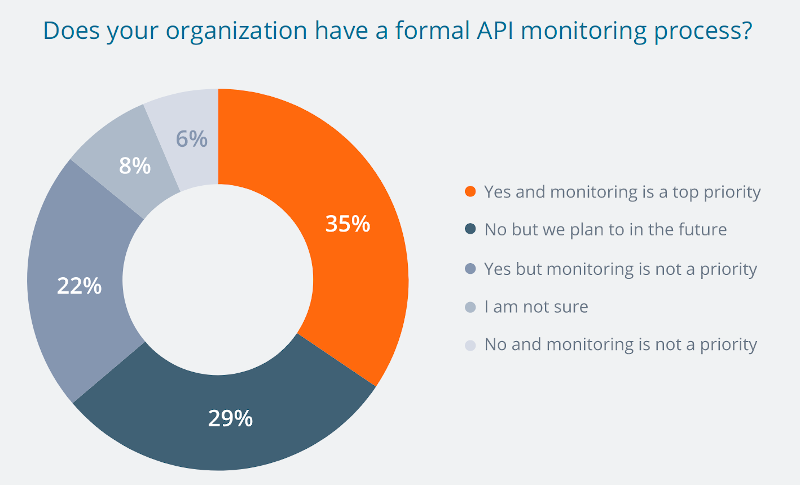
Source: The State of API 2019 by SmartBear
Transport encryption
TLS
- All the web APIs must use HTTPS (TLS)
- Let's Encrypt (open source):
- Domain Validation (DV)
- lifetime 90 day (automatic renew system)
- Paid certificates:
- DV, Organization Validation (OV), Extended Validation (EV)
- lifetime 1 yr and more
HTTPS vulnerabilities
- DROWN attack, March 2016
- Logjam attack, May 2015
- FREAK attack, March 2015
- PODDLE attack, September 2014
- Heartbleed, April 2014
- BEAST attack, September 2011
Authentication &
Access Control
Authentication
- HTTP Basic Authentication
- API Key
- OAuth 2.0 (also authorization)
Authorization
- Authentication is not enough. We need to know who you are!
- OAuth 2.0 provides access control using:
- scope: the subset of information or actions accessible by the key (token)
- validity: a key (token) doesn’t have to be purposely revoked by the system, it will automatically become deprecated in time
Broken Object Level Authorization
- Object-level authorization should be performed for any data coming from API input
- Es. In a blog API, do I have the right to change the title of a post?
PUT /api/post/1234567890 Authorization: Bearer abcdefghi { "title": "Fake title!" } - This is considered the most frequent vulnerability in API Security Top 10 by OWASP
429
- 429 Too Many Requests
HTTP/1.1 429 Too Many Requests Retry-After: 3600 - Use rate limit to maintain control
- Mitigate (Distributed) Denial-of-service attacks
Example: nginx rate limit
limit_req_zone $binary_remote_addr zone=mylimit:10m rate=10r/s;
server {
location /login/ {
limit_req zone=mylimit;
proxy_pass http://my_upstream;
}
}
API gateway
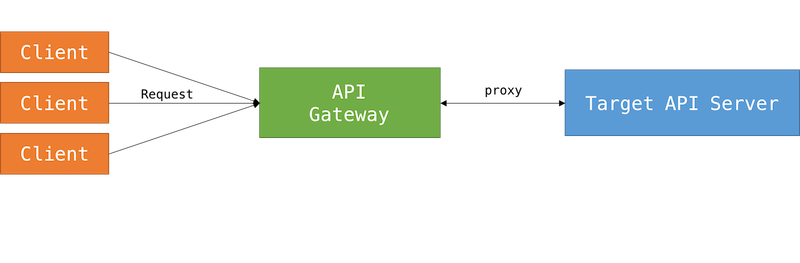
API gateway (2)
- Manage authentication & authorization
- Rate limit
- API inventory
- Caching
- Examples: Apiman, API Umbrella, Gravitee, Kong, Tyk, WSO2 API Management, etc
Storage encryption
Confidential
- Reduce the information to be exposed in API (especially for sensitive data)
- Under GDPR email addresses are considered confidential and must be used and stored within strict privacy and security guidelines
- Encrypt confidential data using standard algorithm (es. AES-GCM-256)
Encryption
Password
- Never store user password in plaintext
- Never store encrypted user password
- Use a password hashing algorithm: argon2
GDPR
- Responsibly store and process data according to risks
- Art. 32, Security of processing
- Art. 35, Data protection impact assessment
Thanks!
Contact me: enrico.zimuel [at] elastic.co
Follow me: @ezimuel

This work is licensed under a
Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International.
I used reveal.js to make this presentation.
